Net Zero
Blueprint
Reducing Emissions with Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt:
A Lifecycle Approach to Decarbonize Road Construction
Reducing Emissions with
Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt:
A Lifecycle Approach to
Decarbonize Road Construction
Decarbonizing Roads with Verde’s Biochar – Asphalt:
A Lifecycle Approach
Key Innovations
Impact
Decarbonizing Roads with Verde’s
Biochar – Asphalt: A Lifecycle Approach


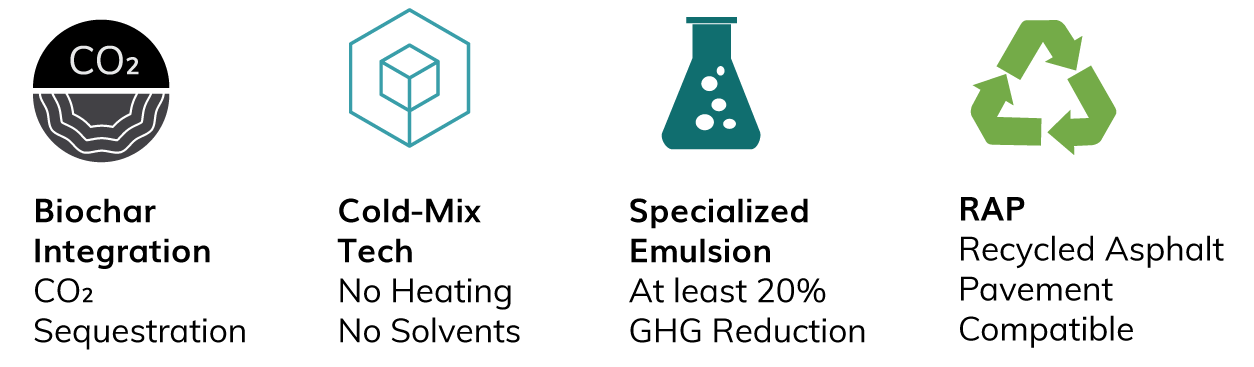
Biochar Integration
CO2 Sequestration
Cold-Mix Tech
No Heating
No Solvents
Specialized Emulsion
At least 20%
GHG Reduction

RAP
Recycled Asphalt Pavement Compatible

Carbon stay locked for
pavement’s life

Align with
decarbonization goals

Suitable for roadways,
parking lots & more

All-Year round
Product
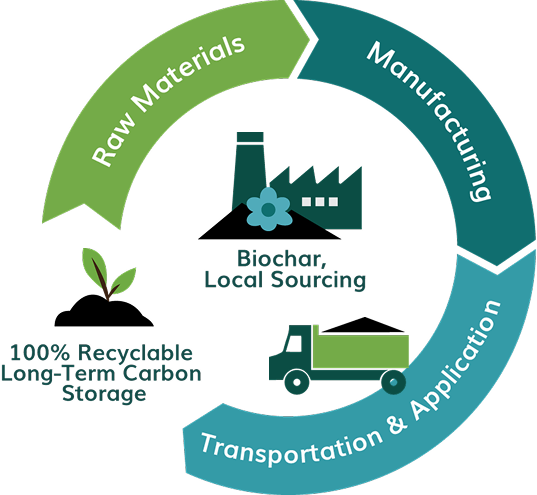
With over 94% of U.S. roads paved with asphalt (FHWA, 2020), the asphalt industry is a key player in both national infrastructure and environmental impact. Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt introduces a powerful path forward—one that lowers greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across the entire product lifecycle by reimagining how asphalt is made, sourced, and applied.
A New Recipe for
Sustainable Roads
Verde’s innovation centers on integrating biochar screenings into its asphalt mix. Biochar, a carbon-rich byproduct of biomass, captures and stores carbon in a stable form. When integrated in asphalt with Verde’s proprietary technology, it effectively sequesters CO₂ for the life of the pavement.
Each mile of road built with Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt—assuming a single lane on each side at 12 feet wide and 2 inches deep—requires approximately 1,500 tons of finished material infused with 75 tons of biochar. This locks away an estimated 135 metric tons of CO₂ equivalent (tCO₂e) per mile over the pavement’s lifespan. For a standard four-lane highway (two lanes in each direction), that sequestration potential doubles to 270 tCO₂e per mile, making Verde’s solution a powerful tool for scalable carbon removal in modern day infrastructure.
But Verde’s sustainability advantages go far beyond carbon capture. By combining cold mix technology with optimized sourcing and installation methods, Verde reduces emissions across every stage of the asphalt lifecycle.
Lifecycle Emissions Reductions:
Scopes 1, 2, and 3
SCOPE 1

Direct Emissions from
Manufacturing
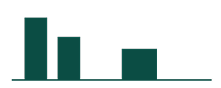
Traditional
Hot-Mix Asphalt
Cold-Mix
Asphalt
Scope 1 – Direct Emissions from Manufacturing
Scope 1 emissions, primarily from the fuel used to heat traditional hot-mix asphalt in plant dryers and burners, account for 30–45% of total emissions in asphalt production. Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt eliminates the need for high-temperature processing, cutting Scope 1 emissions by up to 90%.
Traditional cold mix is costly and primarily used for short-term fixes. Verde’s advanced formulation, independently validated by the National Center for Asphalt Technology (NCAT),
is engineered for broader application. It’s suitable for new construction of low to medium-duty roads, subdivision streets, and parking lots, as well as maintenance and repair of existing heavy-duty roads and similar infrastructure. Additionally, Verde’s proprietary emulsifying agent enables the production of a low-temperature specialized emulsion that emits at least 20% fewer GHGs than conventional binders and seamlessly integrates carbon, forming covalent bonds with aggregates to create a high-performance Biochar-Asphalt surface course.
SCOPE 2

Indirect Emissions from
Electricity

Operational Efficiency
Scope 2 – Indirect Emissions From Electricity
While electricity accounts for a smaller portion of asphalt’s total emissions, turning off burners during mix production and optimizing operational efficiency significantly lowers electricity consumption. This contributes meaningfully to reducing the overall carbon footprint at each mixing plant. The exact percentage reduction is still being quantified and may vary by region.
SCOPE 3

Cold-Mix Asphalt

Raw Materials

Transportation & Installation
Scope 3 – Upstream and Downstream Emissions
Scope 3 emissions, which include raw material extraction, transportation, installation, and end-of-life processing, often account for 30–50% of asphalt’s embodied carbon.
Verde targets these emissions on multiple fronts:
•Local and low-carbon sourcing: Biochar for Verde Asphalt is currently supplied by Oregon Biochar Solutions (OBS). As OBS expands its network, biochar will soon be deliverable within an economical haul distance of asphalt mix plants, significantly cutting transport-related emissions. Other components can still be sourced from existing suppliers, though Verde encourages local sourcing whenever possible.
•Recyclability: Verde’s mix can include Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) and is fully recyclable at the end of its service life.
•Enhanced road performance: The inclusion of biochar may offer added benefits such as reduced in-service temperature. Preliminary data suggest road surfaces made with Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt could remain up to 10°C / 50°F cooler during extreme heat, which would positively affect asphalt binder performance grade (PG) and reduce the risk of tire blowouts. This effect is currently under observation at NCAT.
•Efficiency: Unlike traditional mixes, Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt eliminates the need for heat or solvents during installation. It cuts fuel consumption and on-site emissions dramatically while accelerating project efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Importantly, the carbon stored in Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt remains stable for the life of the pavement as long as it is not incinerated. While incineration is rare in asphalt end-of-life scenarios, avoiding combustion is essential for maintaining the material’s carbon sequestration potential and qualifying for carbon credits.
With over 94% of U.S. roads paved with asphalt (FHWA, 2020), the asphalt industry is a key player in both national infrastructure and environmental impact. Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt introduces a powerful path forward—one that lowers greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across the entire product lifecycle by reimagining how asphalt is made, sourced, and applied.
A New Recipe for
Sustainable Roads
Verde’s innovation centers on integrating biochar screenings into its asphalt mix. Biochar, a carbon-rich byproduct of biomass, captures and stores carbon in a stable form. When integrated in asphalt with Verde’s proprietary technology, it effectively sequesters CO₂ for the life of the pavement.
Each mile of road built with Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt—assuming a single lane on each side at 12 feet wide and 2 inches deep—requires approximately 1,500 tons of finished material infused with 75 tons of biochar. This locks away an estimated 135 metric tons of CO₂ equivalent (tCO₂e) per mile over the pavement’s lifespan. For a standard four-lane highway (two lanes in each direction), that sequestration potential doubles to 270 tCO₂e per mile, making Verde’s solution a powerful tool for scalable carbon removal in modern day infrastructure.
But Verde’s sustainability advantages go far beyond carbon capture. By combining cold mix technology with optimized sourcing and installation methods, Verde reduces emissions across every stage of the asphalt lifecycle.
Lifecycle Emissions
Reductions: Scopes
1, 2, and 3
SCOPE 1

Direct Emissions from
Manufacturing
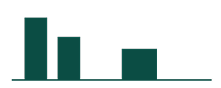
Traditional
Hot-Mix
Asphalt
Cold-Mix
Asphalt
Scope 1 – Direct Emissions from Manufacturing
Scope 1 emissions, primarily from the fuel used to heat traditional hot-mix asphalt in plant dryers and burners, account for 30–45% of total emissions in asphalt production. Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt eliminates the need for high-temperature processing, cutting Scope 1 emissions by up to 90%.
Traditional cold mix is costly and primarily used for short-term fixes. Verde’s advanced formulation, independently validated by the National Center for Asphalt Technology (NCAT), is engineered for broader application. It’s suitable for new construction of low to medium-duty roads, subdivision streets, and parking lots, as well as maintenance and repair of existing heavy-duty roads and similar infrastructure. Additionally, Verde’s proprietary emulsifying agent enables the production of a low-temperature specialized emulsion that emits at least 20% fewer GHGs than conventional binders and seamlessly integrates carbon, forming covalent bonds with aggregates to create a high-performance Biochar-Asphalt surface course.
SCOPE 2

Indirect Emissions from
Electricity

Operational Efficiency
Scope 2 – Indirect Emissions From Electricity
While electricity accounts for a smaller portion of asphalt’s total emissions, turning off burners during mix production and optimizing operational efficiency significantly lowers electricity consumption. This contributes meaningfully to reducing the overall carbon footprint at each mixing plant. The exact percentage reduction is still being quantified and may vary by region.
SCOPE 3

Cold-Mix Asphalt

Raw Materials

Transportation &
Installation
Scope 3 – Upstream and Downstream Emissions
Scope 3 emissions, which include raw material extraction, transportation, installation, and end-of-life processing, often account for 30–50% of asphalt’s embodied carbon.
Verde targets these emissions on multiple fronts:
• Local and low-carbon sourcing: Biochar for Verde Asphalt is currently supplied by Oregon Biochar Solutions (OBS). As OBS expands its network, biochar will soon be deliverable within an economical haul distance of asphalt mix plants, significantly cutting transport-related emissions. Other components can still be sourced from existing suppliers, though Verde encourages local sourcing whenever possible.
• Recyclability: Verde’s mix can include Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) and is fully recyclable at the end of its service life.
• Enhanced road performance: The inclusion of biochar may offer added benefits such as reduced in-service temperature. Preliminary data suggest road surfaces made with Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt could remain up to 10°C / 50°F cooler during extreme heat, which would positively affect asphalt binder performance grade (PG) and reduce the risk of tire blowouts. This effect is currently under observation at NCAT.
• Efficiency: Unlike traditional mixes, Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt eliminates the need for heat or solvents during installation. It cuts fuel consumption and on-site emissions dramatically while accelerating project efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Importantly, the carbon stored in Verde’s Biochar-Asphalt remains stable for the life of the pavement as long as it is not incinerated. While incineration is rare in asphalt end-of-life scenarios, avoiding combustion is essential for maintaining the material’s carbon sequestration potential and qualifying for carbon credits.
Conclusion: A Scalable,
Common-Sense Solution
Designed for year-round applications including winter in any location where stockpiles are not frozen or unworkable, Verde’s solution enhances profitability while enabling large-scale carbon sequestration using existing infrastructure. From production through end-of-life, Verde delivers a high-performance and sustainable alternative that cuts emissions across all three scopes, generates carbon credit revenue as a bonus, and drives substantial economic impact, all while modernizing infrastructure in the era of decarbonization mile by mile.
Conclusion: A Scalable,
Common-Sense Solution
Verde’s licensable Biochar-Asphalt Blueprint empowers existing hot mix producers to seamlessly #TransitionToZero™, eliminating the need for energy-intensive burners and dramatically cutting GHG emissions. This transition requires minimal changes to existing equipment or supply chains, preserving vendor relationships and reducing costs that directly improve their bottom line.
Designed for year-round applications including winter in any location where stockpiles are not frozen or unworkable, Verde’s solution enhances profitability while enabling large-scale carbon sequestration using existing infrastructure. From production through end-of-life, Verde delivers a high-performance and sustainable alternative that cuts emissions across all three scopes, generates carbon credit revenue as a bonus, and drives substantial economic impact, all while modernizing infrastructure in the era of decarbonization mile by mile.